Since the seafood company would never leave older inventory in stock to spoil, FIFO accurately reflects the company’s process of using the oldest inventory first in selling their goods. As a result, LIFO isn’t practical for many companies that sell perishable goods and doesn’t accurately reflect the logical production process of using the oldest inventory first. Below is a break down of subject weightings in the FMVA® financial analyst program. As you can see there is a heavy focus on financial modeling, finance, Excel, business valuation, budgeting/forecasting, PowerPoint presentations, accounting and business strategy. We offer a broad range of services to help clients secure a sound financial future.
FIFO Tax Implications
The choice between FIFO and LIFO significantly influences a company’s financial statements, particularly the income statement and balance sheet. When a company uses FIFO, the cost of goods sold (COGS) reflects older, often lower costs, especially in times of inflation. This results in higher gross profits and, consequently, higher net income.
LIFO and FIFO: Taxes

Even if a company produces only one product, that product will have different cost values depending upon when they produce it. When inventory is acquired and when it’s sold have different impacts on inventory value. Cost of Goods Sold, or COGS, is the amount of money a business pays to produce the number of goods sold in a given period. The products that are left in the warehouse are called remaining inventory. The LIFO system is founded on the assumption that the latest items to be stored are the first items to be sold.
- Regular inventory turnover tends to keep inventory value closer to market value and is a more realistic representation of how most companies move their products.
- In other words, the older inventory, which was cheaper, would be sold later.
- Here is a high-level summary of the pros and cons of each inventory method.
Saving taxes
So, which inventory figure a company starts with when valuing its inventory really does matter. And companies are required by law to state which accounting method they used in their published financials. However, please note that if prices are decreasing, the opposite scenarios outlined above play out. In addition, many companies will state that they use the “lower of cost or market” when valuing inventory. This means that if inventory values were to plummet, their valuations would represent the market value (or replacement cost) instead of LIFO, FIFO, or average cost.
LIFO: Items bought last will be sold first
The firm offers bookkeeping and accounting services for business and personal needs, as well as ERP consulting and audit assistance. Despite increasing production costs, Company A retains a consistent sales price of $400 per vacuum. They sell 200 vacuums in the first quarter, generating a revenue of $80,000. This makes it easy for business owners to manage their accounting and makes it simple for investors to interpret the financial statements. FIFO is an accepted method under International Financial Reporting Standards.
FIFO inventory valuation
Finally, standard costing will provide a focus on cost control and overall planning for any organization, and usage is heavily concentrated on large manufacturing organizations. All four of the listed methodologies offer distinct benefits, making it important for management to assess which option aligns best with the strategic direction of their company. Choosing among weighted average cost, FIFO, or LIFO can have a significant impact on a business’ balance sheet and income statement. Businesses would select any method based on the nature of the business, the industry in which the business is operating, and market conditions. Decisions such as selecting an inventory accounting method can help businesses make key decisions in relation to pricing of products, purchasing of goods, and the nature of their production lines. Inventory costing remains a critical component in managing a business’ finances.
When a company selects its inventory method, there are downstream repercussions that impact its net income, balance sheet, and ways it needs to track inventory. Here is a high-level summary of the pros and cons of each inventory method. All pros and cons listed below assume the company is operating in an inflationary period of rising prices. In contrast, the LIFO inventory valuation method results in a higher COGS so the company can claim a greater expense. Higher reported gross income also leads to an inflated representation of profits. A company generates the same amount of income and profits regardless of whether they use FIFO or LIFO, but the different valuation methods lead to different numbers on the books.
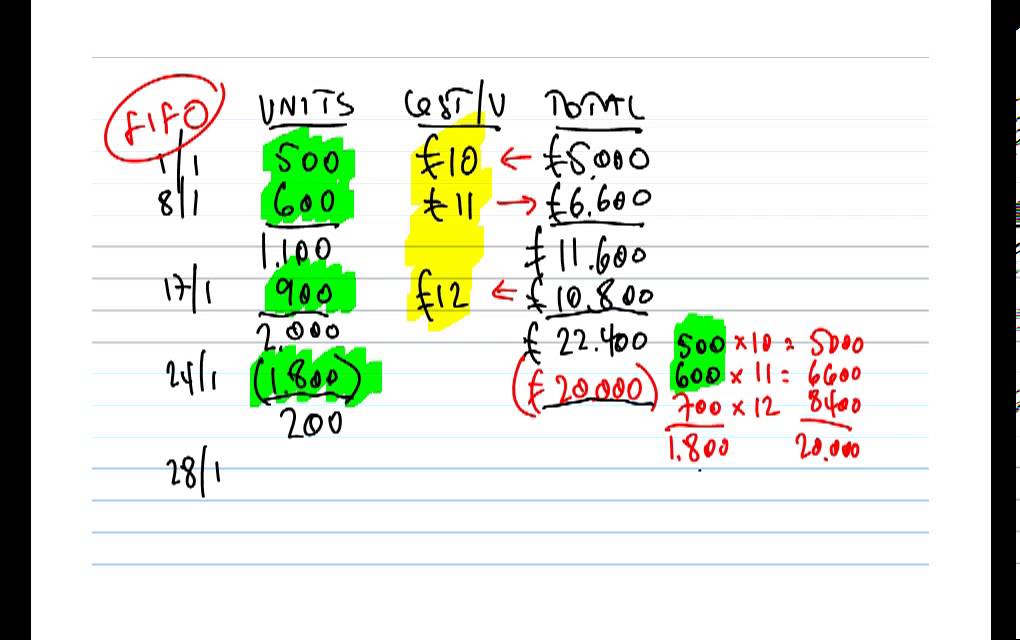
Again, these are short-term differences that are eliminated when all of the shirts are sold. Inflation is the overall increase in prices over time, and this discussion assumes that inventory items purchased first are less expensive than more recent purchases. Since the economy has some level of inflation in most years, prices increase from one year to the next. In the tables below, we use the inventory of a fictitious beverage producer called ABC Bottling Company to see how the valuation methods can affect the outcome of a company’s financial analysis. In addition to being allowable by both IFRS and GAAP users, the FIFO inventory method may require greater consideration when selecting an inventory method.
FIFO and LIFO are helpful tools for calculating the value of your business’s inventory and Cost of Goods Sold. FIFO assumes that your oldest goods are sold first, while LIFO assumes that your newest goods are sold first. Learn more about what LIFO is and its impact on net income to decide if LIFO valuation is right for you. Let’s say on January 1st of the new year, what is a balance sheet forecast Lee wants to calculate the cost of goods sold in the previous year. Tanner joined McKonly & Asbury in 2022 and is currently a Senior Accountant with the firm’s Assurance & Advisory Segment, servicing our Manufacturing and Nonprofit clients. Regardless of the price you paid for your wire, you chose to keep your selling price stable at $7 per spool of wire.
For example, suppose a hypothetical scenario, where the inventory purchased earlier is less expensive compared to recent purchases. Accounting for inventory is essential—and proper inventory management helps you increase profits, leverage technology to work more productively, and to reduce the risk of error. You should also know that Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) allow businesses to use FIFO or LIFO methods. However, International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) permits firms to use FIFO, but not LIFO. Check with your CPA to determine which regulations apply to your business.
Of these, let’s assume the company managed to sell 3,000 units at a price of $7 each. What should be the unit cost used to determine the value of this unsold inventory? The choice between FIFO and LIFO extends beyond financial statements, deeply influencing a company’s tax obligations. Under FIFO, the lower cost of goods sold during inflationary periods results in higher taxable income. This can lead to a substantial tax burden, which might strain cash flow, especially for businesses with tight margins.